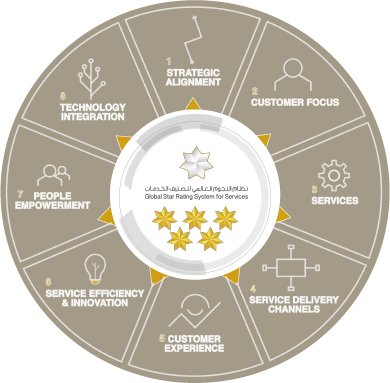
Global Stars System For Services
The Global Star Rating System is a methodology that rates service channels on a scale of 2 to 7 stars based on the outcome of independent evaluation and assessment of customer experience. The system helps both government and private entities to measure, improve and transform the way they manage, operate, and provide services to citizens and residents across all touchpoints. The system is based on 8 main pillars, supported by 35 sub-pillars covering the customers’ experience and journey from all angles, including customer experience, service efficiency, innovation, human resource empowerment, integrated technology, and others.
The development of the global star system for rating services is one of the initiatives emanating from the Emirates Program for Excellence in Government Service. This program aims to improve the quality of government and private services by focusing on customer centric services, employee happiness, and improving operational efficiency, to provide high-quality seven-star services. This integrated system is the first of its kind in the world, and although it was launched in the United Arab Emirates, it sets a world-class standard that helps government and private entities measure, improve and transform the field of service provision.
Some Examples of Key Deliverables:
- Experimental evaluation of all customer happiness centers.
- A survey report on employees and frontliners’ awareness about the program.
- Identify the list of outputs for each sub-criterion of the service development system.
- Building and updating program documentations including operational processes, SOPs, manuals and guidelines for happiness centers management.
- Center performance analysis and reporting schemes.
- Building and updating marketing and communication plans.
- Assessing the customer experience and providing relevant analytical, technical studies, Improvement initiatives and recommendations .
- Assenting detailed customer happiness perceptions, preferences and needs.
- Building operational work plans
- Building service delivery improvement plans including customized implementing projects and initiatives based on program requirements.
- Technical support in preparing program documentation.
- Building and Updating Customer Data including Customer Persona Profiles, Classifications, Categories and Emotional Patterns.
- Provide systematic studies related to capacity planning and workforce forecasting for optimum resources utilization.
PILLARS
SUB PILLARS
ASSESMENT AREAS
It is a comprehensive assessment of eight main pillars and 35 sub-pillars that include several criteria that cover points related to the development and delivery of services. These eight axes aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the customer’s experience across multiple channels of service delivery.
This system is designed based on international best practices from the government and private sectors, with a great focus on involving the customer in developing the service and ways to provide it through joint design and electronic participation. The evaluation also covers some of the main topics included in the United Nations e-government survey, including emerging technology, digital inclusion, open data, and cybersecurity.
Some Key Deliverables Per Main Pillars
Strategic Alignment
- Measuring the leadership’s awareness of the importance of developing the customer experience
- The service development strategy is linked to the master strategic plan
- Forming service development team
- MOMs of Service development team
- Service development initiatives within the Center’s operational plan.
- Communication plan of Service development team.
- Quarterly report on the achievements.
- Employee participation in social responsibility initiatives
- A digital system for initiatives and followup on their implementation
Customer Focus
- The availability of Customer Happiness Charter on all channels with indicators to measure the charter and measure results at all employee levels
- Charter training workshops
- Focus groups with customers
- Measurement of specific costs and benefits
- Analyzing big data for customers on all channels
- Customer participation in the development of services (workshops)
- Innovation labs (service development)
- Upgrading customer reports in cooperation with stockholders
Services
- Service classification at transactional level.
- Review and enhance the services catalog across all channels according to the system requirements.
- Review/Redesign service bundles.
- Setting standards for service performance and measures.
- Reviewing and developing the complaints system within specific performance measures.
- Assessing digital services and KPIs.
- Assessing call center services and KPIs.
- Review/Update marketing strategy and measuring the impact of marketing campaigns.
- Assessing customers’ communications
Technology Integration
- Building systematic capacity and forecasting planning.
- Measuring the CX impact
- Assessing of the POD accessibility for physical happiness centers, the website (AAA) and smart.
- Studying service integration across all service channels
- Building improvement plans for encouraging digital adoption by customers.
Customer Pain Points
- Building unified system for customer transactions
- Review the customer data analysis reports and studies.
- Determine the percentage of automation of front office and back-office operations
- Determine the associated system integration with other parties
- Studying emerging technologies that may help in the future.
- Building knowledge management system.
- Review the information security policy
- Review the open data policy.
- Review the digital security protocols
- Review customer data security plan
- Training on information security
People Empowerment
- Ensure employee participation in the service development.
- Review Job descriptions and competencies for employee.
- Training plan includes soft and technical skills.
- Training on problem solving.
- Reviewing the performance appraisal system for employees.
- Employee Appreciation and awarding scheme.
- Review employee happiness measures and assessing the impact of employee happiness initiative.
- Building methodology of knowledge transfer identifying mentors and counseling processes.
Service Efficiency and Innovation
- Defining service-related processes and process quality standards
- Operations improvement plan
- Service continuity plan
- Review Service Level Agreements (SLAs) and measures
- Methodology for rating partners and measuring partner satisfaction
- Identify shared services and their measures.
- Review performance management system.
- Encouraging employees and customers, such as digital channels and social media.
Customer Experience
- Assessing current customer experience.
- Defining the optimum customer’s experience based on customer persona across all service delivery channels including website, call center and smart channels.
- Building improvement plans to enhance current customer experience
- Build quantitative and qualitative data resources to provide continues feedback loop for sustainable performance of intended customer experience.

Some Key Deliverables of As-is Assessment Phase
Data inputs analysis
OUTPUT
Summary including initial inventory of available data and areas of focus in the self-assessment process
Self-Assessment
OUTPUT
Self-Assessment feedback reports
Discussing Sefl-Assessment feedback reports
OUTPUT
Summary including initial inventory of available data and areas of focus in the self-assessment process
Prepare Work Plans
OUTPUT
Customized Full operational plans per centre covering all gaps defined in the feedback assessment report
Main Elements of Centers’ Operational Plans
Main Elements
Frontliners Performance
Adherence KPIs
Corporate Document at Centers’ Level
Description
Balanced Scorecard (BSC) for each frontliner and supervisor
Measuring the adherence to plans implementation as per the expected outputs
Including planes, MOMs, Or any other documentation required by the Global Star Rating System
Approach
Determining the type of responsibility based on the specific nature of each pillar of the operational plan that is at the preparation phase.
Follow Up Mechanism
Expected Impact
Ensure sustained quality performance by the frontliners and supervisors
Increase readiness for actual assessment
Increase readiness for actual assessment
Enhancing Customer Experience
We managed to design comprehensive customer experience to reach the ultimate total experience. Here are some examples of key deliverables:
- Collect, and review existing service catalogue studying digitization applicability as per best practices
- Automating applicable back-office services
- Eensure service integration readiness including digital identity logging and automated payments channels.
- Provide support service delivery channels as alternative for digital channels as per customer preferences.
- Study existing services are applicable to transform into proactive services.
- Re-Design proactive services based on actual customer needs
- Studying the potential for integration with strategic partners or merger for some services.
- Studying existing service systems and data.
- Review service requirements (from customer perspective).
- Technical improvement on services’ systems building on service integration to provide seamless service delivery
- Revised data security and privacy criterion, and ensure alignment with required development processes
- Studying existing customizable services based on customers needs.
- Studying shared service delivery channels (if any) for effective service delivery procedures.
- Collect, and review existing service KPIs and measures including SLAs.
- Study feasibility of providing services though unified/centralized digital channels
- Leveraging digital channels enhancements based on voice of customer, considering seamless customer experience.
- Ensure current continuous improvement procedures consider customer needs and expectation
- Design integrated and innovative future customer journeys
- Assessing current maturity level according to ICX standers.
- Prepare enablement plans for service advisors
- Review service information update procedures across all relevant systems
- Improve support systems to enable service advisors providing customer service safely and securely
One of our deliverables for total customer experience was conducting CX Maturity Assessment as per International Customer Experience Institute (ICXI):
Policies, Places, Services, Processes, CJs, People, Measurement Performance and Performance Results
where each of main criteria has a couple of sub-assessment criteria.
Without fulfilling those requirements entity won’t be complying with ICX
Standard Level (55 – 74.9%)
Benchmark Level (75 – 89.9%)
International Excellence Level (+90%)
At INBSPIRED EXPERTS, we had a great teams of Senior Consultants and Subject Matters Experts helped to provide their valuable site assessment and recommendations:
The policy has set a number of ambitious goals which include:
- 100 per cent proactive and automated services
- 90 per cent integrated services
- 90 per cent service provision without the physical presence of the customer.
As for the targets concerned with service delivery channels, the policy is aiming for:
- 100 per cent conversion to shared channels
- 95 per cent self-services
- 95 per cent digital adoption
- 90 per cent average channel evaluation.
Under the implementation of the Services 360 policy, it is expected to:
- achieve annual financial savings
- eliminate physical customer visits to service centers
- free up working hours within the entities due to increased operation efficiency.
Service Design Framework
Background
Governments provide a wide range of services to citizens, from healthcare and education to social security and public safety. However, traditional approaches to service delivery have been fragmented, siloed, and reactive, resulting in inefficiencies, duplication, and frustration for both citizens and government officials. Service design can help address these challenges by creating a user-centric, integrated, and proactive service delivery system.
In recent years, governments around the world have been exploring new ways to improve the quality and efficiency of their services. Service design has emerged as a promising approach, with its emphasis on co-creation, prototyping, and continuous improvement. By applying service design principles, governments can identify the needs and expectations of citizens, design services that meet those needs, and measure the impact of those services.
Objective, Methodology and Results
Objective:
The objective of this case study is to develop a service design framework for improving government services, with a focus on ensuring seamless, integrated, proactive, and customized services. The framework should address the challenges and opportunities of service delivery in the government context and provide actionable insights for implementing innovative solutions.
Methodology:
The service design methodology used for this case study includes the following steps:
Research: Conduct interviews, surveys, and desk research to understand the needs and pain points of citizens, as well as the challenges and opportunities facing government agencies.
Ideation: Develop a range of potential solutions based on the research findings, using tools such as brainstorming and mind mapping.
Prototyping: Create prototypes of the most promising solutions, and test them with citizens and government officials to gather feedback and insights.
Implementation: Develop a roadmap for implementing the solutions, including a timeline, budget, and stakeholder engagement strategy.
Results:
The service design framework developed for improving government services includes the following components:
User research: Conduct user research to identify the needs, expectations, and pain points of citizens, and use this information to inform service design.
Service mapping: Map the service journey from the citizen’s perspective, identifying pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Co-creation: Involve citizens and government officials in the co-creation of new services, using tools such as design sprints, hackathons, and workshops.
Service delivery: Use digital technologies and other tools to streamline service delivery, reduce bureaucracy, and improve the user experience.
Continuous improvement: Continuously monitor and evaluate services, using feedback and data analytics to inform service design and delivery.
Service design can help governments create a more user-centric, integrated, and proactive service delivery system. By identifying the needs and expectations. The framework developed in this case study provides a roadmap for implementing service design in the government context and can serve as a model for other government entities seeking to improve their services.
Adopting Future Technologies
Background
Governments around the world are under pressure to adopt new technologies to improve the quality and efficiency of their services. From artificial intelligence and blockchain to the Internet of Things and 5G, there are a wide range of emerging technologies that can be used to transform government services. This case study explores how one government agency adopted future technologies to improve the delivery of its services.
The government agency in question is responsible for managing public transportation in a major metropolitan area. The agency faced several challenges in delivering its services, including outdated technology, high operational costs, and low customer satisfaction. To address these challenges, the agency decided to adopt a range of future technologies, including IoT, AI, and blockchain.
Objective, Methodology and Results
Objective:
The objective of this case study is to demonstrate how the adoption of future technologies can improve the quality and efficiency of government services, using the example of a public transportation agency.
Methodology:
The methodology used for this case study includes the following steps:
- Needs assessment: Identify the needs and pain points of the agency and its customers and develop a roadmap for addressing them.
- Technology assessment: Identify the emerging technologies that could be used to address the agency’s needs, and evaluate their feasibility, cost, and potential impact.
- Implementation: Develop a plan for implementing the selected technologies, including a timeline, budget, and stakeholder engagement strategy.
- Evaluation: Monitor and evaluate the impact of the new technologies on the agency’s operations and customer satisfaction and adjust as needed.
Results:
The adoption of future technologies had several positive impacts on the services:
- Improved operational efficiency: The agency was able to monitor its vehicles and infrastructure in real-time using IoT sensors, which allowed it to optimize its operations and reduce costs.
- Improved customer experience: Implemented AI-powered chatbots and mobile apps to provide customers with real-time information about routes, schedules, and delays, which improved customer satisfaction and reduced complaints.
- Improved security and transparency: The agency used blockchain to create a secure and transparent system for managing payments and transactions, which reduced fraud and improved trust among customers.
- Improved data analytics: AI and big data analytics to analyze customer feedback & usage patterns, helped identify areas for improvement and data-driven decisions.
The adoption of future technologies can improve the quality and efficiency. By identifying the needs and pain points of customers, and selecting the technologies that best address those needs, governments can deliver services that are more efficient, transparent, and user-friendly. However, the adoption of future technologies requires careful planning, stakeholder engagement.
We build Impactful, Innovative and Sustainable business practices
Our team of experienced consultants works closely with corporate and organizational leaders to identify opportunities for growth and develop tailored strategies that align with their unique goals and values.
We believe that true success is not just about short-term financial gains, but about creating long-term value for our customers, their stakeholders, and the wider community. To achieve this, we prioritize sustainability in everything we do, from our approach to problem-solving to the technologies and tools we use.
Our focus on innovation means that we are constantly exploring new ideas, methods, and technologies to help our customers stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge. We understand that the business landscape is constantly evolving, and we are committed to staying on top of emerging trends and adapting our strategies accordingly.
But innovation alone is not enough. We also prioritize impact, ensuring that our strategies create real, measurable outcomes for our customers and the communities they serve. We work closely with our customers to define their key performance indicators and track progress against these metrics, providing regular updates and transparent reporting throughout the engagement.